Smart Home Compatibility Checker
Check if your smart devices work together! Test compatibility with Alexa, Google Home, and more in seconds with our free tool.
Analyzing network traffic can enhance performance, identify bottlenecks, and boost security through effective monitoring and data analysis.
Want a faster, more reliable network? Start by analyzing your network traffic. This process helps identify slowdowns, optimize performance, and strengthen security by monitoring how data flows through your network. Whether you're managing a home WiFi or a business setup, understanding key metrics like bandwidth, latency, and packet loss can make all the difference.
If you're stuck, professional services like TekDash can assist with diagnostics, setup, and maintenance, ensuring your network performs at its best.
Selecting the right data collection method depends on your network's size, specific needs, and technical setup. Two primary approaches are agent-based monitoring, which involves installing software on devices, and agentless monitoring, which gathers data remotely.
These two methods cater to different network configurations. Agent-based monitoring requires software installation on each device, while agentless monitoring relies on standard protocols to collect data without additional software.
| Feature | Agent-Based Monitoring | Agentless Monitoring |
|---|---|---|
| Deployment | Installs software on each device | Uses existing network protocols and APIs |
| Setup Speed | Slower; manual installation required | Quick setup after initial configuration |
| Scalability | Limited; each device needs setup | Highly scalable; auto-discovers new devices |
| Security | Ideal when credentials cannot be shared | Requires credentials but avoids software setup |
| Resource Impact | May impact device performance | No performance impact on monitored devices |
| Maintenance | Needs regular updates and management | Managed by the service provider |
Agent-based monitoring is ideal when sharing network credentials is not an option, when monitoring devices in distributed locations with changing IPs, or when you need uninterrupted data collection even if the central server goes offline. It operates through a single HTTPS outbound connection and avoids enabling additional protocols like SNMP or WMI.
On the other hand, agentless monitoring is well-suited for servers, switches, and routers, especially in virtualized setups where installing extra software is not practical. Many organizations use a mix of both methods to achieve a balanced approach, combining visibility with security.
Network monitoring relies on standardized protocols that help devices share status and performance data. Here are some key protocols:
Using tools that support multiple protocols can provide a more holistic view of network health by leveraging the strengths of various methods.
Relying on a single data source can leave gaps in understanding your network. Combining different types of data - flow, packet, and logs - offers a more complete picture.
This layered approach is particularly useful during incident investigations. For example, flow data might highlight communication with a suspicious IP, packet analysis could show the nature of the traffic, and logs might clarify what initiated the activity. Many modern network platforms integrate these sources with IT systems like SIEM tools and ticketing platforms, presenting all data in a unified dashboard.
Integrating multiple sources not only strengthens network monitoring but also sets the stage for identifying performance baselines and making targeted improvements in future steps.
Once you've gathered your data, the next step is to establish a performance baseline. This baseline serves as a snapshot of your network's typical behavior under normal operating conditions. With more than 90% of companies globally relying on cloud services and the Internet of Things generating nearly 80 zettabytes of data annually from over 18 billion connected devices, having a clear baseline is essential. Here's how to set one up and make the most of it.
To create a reliable baseline, collect data over different timeframes. This approach helps you capture a comprehensive view of your network's hardware, software, and overall configuration. Monitor your network during regular business hours, weekends, and peak usage times to account for varying conditions. Pay close attention to metrics that directly influence performance.
Key metrics to include in your baseline are bandwidth usage, latency, jitter, packet loss, throughput, and application performance. These measurements help you define threshold levels and establish benchmarks for future comparisons. Document everything thoroughly to ensure you have a solid reference point.
Choosing the right metrics is critical for identifying potential issues before they escalate. For example:
By focusing on these areas, you can quickly detect problems and reduce user frustration.
To keep your baseline accurate, it's essential to use both real-time and historical data. Real-time data offers immediate insights into network performance, utilization, and security events. This allows administrators to spot anomalies as they happen and take action quickly. For example, if a metric exceeds its threshold, you can address the issue before it impacts users.
Historical data, on the other hand, helps you identify long-term trends. By examining past performance, you can uncover recurring issues or gradual changes in network usage. For instance, you might detect periodic slowdowns linked to scheduled tasks or notice a steady increase in traffic over time. Many organizations have used historical data to resolve recurring problems more effectively.
Combining real-time and historical analyses gives you a proactive edge. This strategy is especially important given that, in 2023, 91% of businesses worldwide experienced at least one outage per quarter, with over two-thirds of these outages costing more than $100,000. Regularly updating your baseline ensures it reflects new devices and evolving usage patterns.
A well-maintained network baseline not only helps you diagnose issues faster but also validates network upgrades and pinpoints potential bottlenecks. Considering that 51% of employees cite slow network speeds as their top technology complaint, maintaining clear baselines and metrics is key to boosting productivity and user satisfaction.
Once you've established a baseline and set up metrics, it's time to identify where your network might be falling short. Bottlenecks happen when the network's capacity can't keep up with the current traffic load. Considering that 74% of network professionals acknowledge that network changes significantly affect business operations, it's crucial to tackle these issues promptly to keep productivity on track. This sets the stage for identifying and resolving performance challenges effectively.
The best way to spot bottlenecks is by comparing your current network performance against your baseline. Network monitoring tools help by analyzing performance data, offering insights into latency, packet loss, and traffic patterns. If you notice deviations from your normal metrics, it’s a sign that something needs attention.
Start by using packet capture to identify unusual data flows. Tools like NetFlow are particularly valuable because they provide a detailed view of traffic patterns, showing bandwidth usage by applications and protocols, and tracking where traffic originates and ends.
Keep an eye on these critical metrics to catch bottlenecks early:
Reliable monitoring tools can pinpoint bandwidth bottlenecks, identify which applications or endpoints are consuming the most bandwidth, and even analyze historical data to detect recurring issues. Many tools also allow you to set alerts for high bandwidth usage.
Distinguishing between normal network fluctuations and real performance problems requires careful analysis of your data. Real-time monitoring helps detect immediate issues, while historical data provides insights into long-term trends.
Pay attention to these key performance indicators:
Once you've identified the problem areas, you can apply targeted solutions. Typical bottleneck causes include bandwidth constraints, outdated hardware, overloaded interfaces, misconfigurations, application performance issues, and shared network resources.
Consistently monitoring traffic patterns, interface utilization, and packet loss will help you stay ahead of potential issues. By addressing these problems proactively, you can ensure smooth network operations and avoid costly disruptions.
While tackling network problems on your own can often resolve minor issues, more complex setups and recurring performance problems call for professional expertise.
If basic troubleshooting doesn’t resolve the problem, or if you’re dealing with ongoing network disruptions or potential security threats, it’s time to bring in an expert. Here’s when professional help becomes crucial:
Complex Infrastructure Issues demand specialized knowledge. When your network includes enterprise-level equipment, multiple segments, or advanced configurations, expert intervention ensures everything runs smoothly. This is especially critical for networks spanning multiple locations or involving specialized hardware like managed switches or enterprise-grade firewalls.
Persistent Performance Problems that don’t improve with typical fixes, such as upgrading hardware or tweaking configurations, often point to deeper issues. In such cases, professionals can conduct in-depth diagnostics to uncover and resolve the root causes.
Security Concerns should never be ignored. With 96% of business leaders emphasizing the importance of cybersecurity resilience, any unusual activity or suspected breach requires immediate expert evaluation. Professionals are equipped to spot threats that might go unnoticed by those without specialized training.
If your in-house IT team lacks the capacity or expertise to handle these challenges, professional services can step in to bridge the gap. It’s worth noting that 57% of IT teams report limited visibility into their network configurations, which can hinder effective troubleshooting.
To help professionals address your issue quickly, provide as much information as possible - describe the problem, include error messages, note recent changes, and list any fixes you’ve already tried.
For those in need of expert assistance, TekDash offers solutions tailored to these exact scenarios.
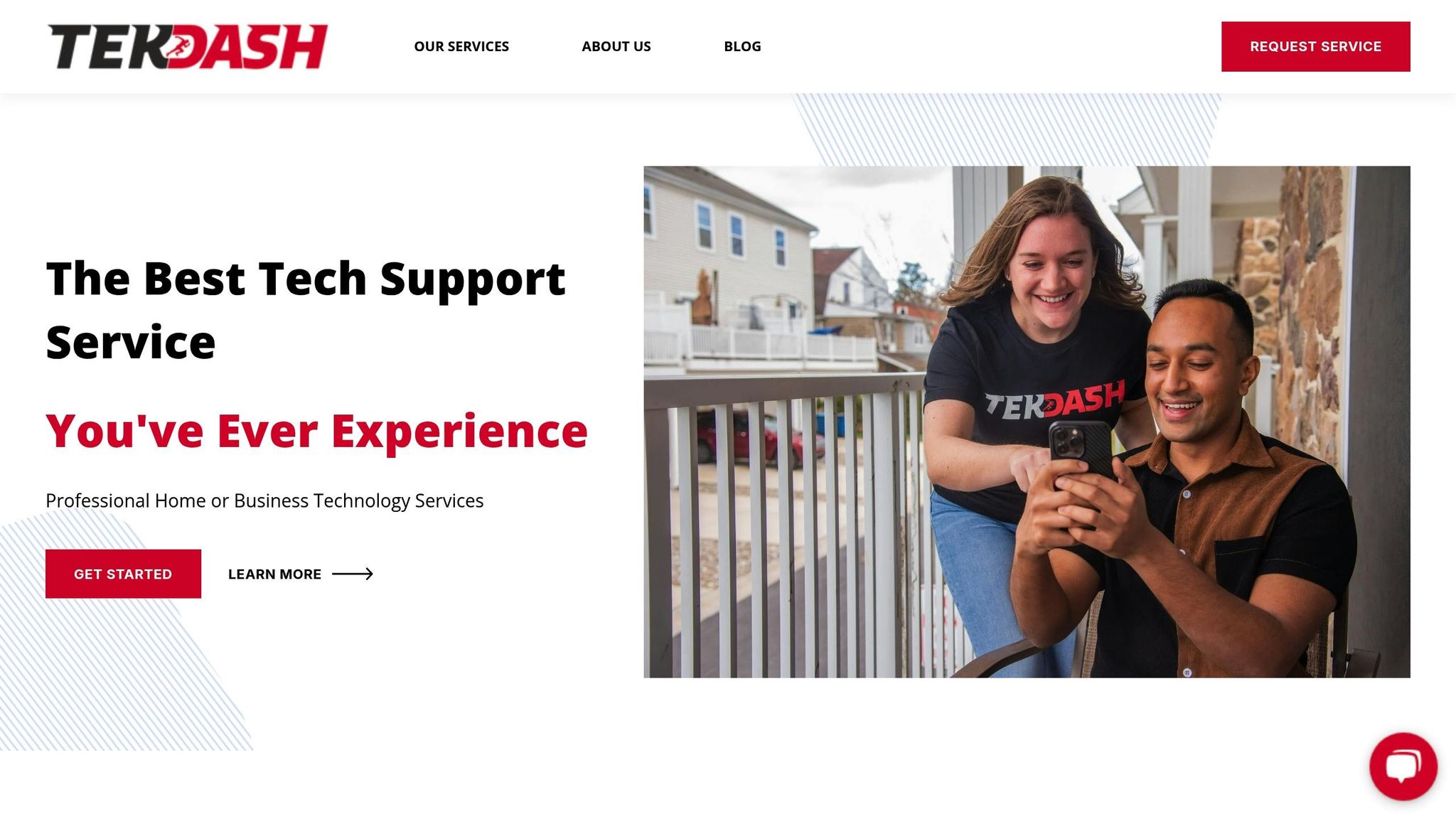
TekDash provides both on-site and remote services to optimize networks for homes and businesses. Their certified technicians specialize in diagnostics, installation, and ongoing maintenance to ensure your network performs at its best.
Network Diagnostics and Troubleshooting are at the heart of TekDash’s offerings. Their team conducts thorough diagnostics to pinpoint bottlenecks, connectivity issues, and other hidden problems. This approach ensures they address the underlying causes, not just the symptoms.
Infrastructure Installation and Optimization includes everything from Ethernet cable installation and WiFi setup to extending wireless signals. TekDash handles the entire process, from designing the network to certifying Ethernet line speeds, ensuring your wired connections meet performance standards.
Smart Home Integration is another key service, as more devices rely on home networks. TekDash assists with installing and configuring smart devices like thermostats, security cameras, and video doorbells. Proper setup is crucial to prevent these devices from creating network slowdowns or vulnerabilities.
TekDash also offers proactive maintenance to prevent issues before they disrupt your productivity, alongside reactive troubleshooting for immediate concerns. Their transparent pricing structure ensures there are no surprises, whether you choose remote or on-site services.
"Network optimization isn't about performance; it's also a strategic investment that allows you to properly allocate resources." - BTI Group
This professional approach is invaluable when considering that 91% of employees report frustration with inadequate workplace technology, citing slow speeds and delayed IT responses as major pain points. By enlisting expert services, you can sidestep these issues, improving productivity and reducing user frustration.
Network traffic analysis serves as a vital tool for evaluating the health and performance of your network. Let’s break down the essential steps and insights covered earlier.
Analyzing network traffic effectively requires a structured approach to turn raw data into meaningful insights. The first step is selecting the right data sources - whether it’s flow data, packet data, or WiFi data - each offering distinct perspectives on network behavior.
Establishing baselines is crucial. By setting benchmarks and monitoring key metrics like bandwidth, latency, jitter, and packet loss, you can quickly identify any unusual activity. For example, tracking these metrics allows you to detect issues like sudden bandwidth spikes or increased latency before they escalate, ensuring critical applications run smoothly.
Continuous monitoring is equally important. It minimizes blind spots and supports early detection of potential security threats, protecting your network from vulnerabilities.
As a reflection of its growing importance, the network traffic analytics market was valued at $2.92 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow to $3.32 billion in 2024. This underscores just how essential these practices are in managing modern networks.
While understanding the basics of network analysis is valuable, implementing advanced monitoring and optimization often calls for professional expertise. That’s where TekDash steps in.
TekDash provides a team of certified technicians who excel in diagnosing network issues and optimizing performance. Their focus isn’t just on fixing symptoms but on tackling the root causes of problems.
They also handle the physical side of network performance. From expert Ethernet cable installations to WiFi setup, TekDash ensures your infrastructure is ready to support efficient traffic analysis and maintain top-notch performance.
With remote services starting at $60 and on-site services beginning at $145, TekDash offers clear pricing for both immediate fixes and ongoing network maintenance.
Combining agent-based and agentless monitoring creates a well-rounded approach to analyzing network performance. With agent-based monitoring, you gain detailed, real-time insights by gathering data directly from devices. This method provides precise control and a deeper level of visibility. Meanwhile, agentless monitoring simplifies deployment, covers a wider range of the network, and uses fewer resources, making it ideal for large-scale systems.
When these two methods work together, they can strengthen network security, enhance monitoring precision, and increase operational efficiency. This hybrid strategy takes advantage of the unique benefits of both approaches, offering a more complete picture of your network's health and performance.
To get the most out of your network, keep an eye on key metrics like bandwidth usage, latency, packet loss, and jitter. These metrics reveal how well your network is performing and can help you spot potential trouble areas before they become major issues.
It’s also worth monitoring other metrics such as throughput, error rates, and round-trip time (RTT). By regularly reviewing these, you’ll gain deeper insights into your network’s performance and be able to address any problems quickly to keep things running smoothly.
Need help with setting up or troubleshooting your network? TekDash provides expert services to ensure your network operates without a hitch.
If you're constantly running into connectivity issues, experiencing sluggish internet speeds, or struggling with a tricky network setup, it might be time to call in the pros. TekDash offers a range of expert services, including network troubleshooting, WiFi and Ethernet installation, boosting WiFi signal coverage, and setting up smart home devices. Their certified technicians focus on providing quick, reliable solutions customized to fit the specific needs of your home or business.
Check if your smart devices work together! Test compatibility with Alexa, Google Home, and more in seconds with our free tool.
Learn how to set up a reliable home network with this step-by-step guide. Perfect for beginners and advanced users alike.
Learn how to set up your router and enhance home network security with simple tips for IP addresses, DNS settings, and device management.